The constructor in Java is a special method type that is used to initialize objects. Constructor is summoned at object creation time. It constructs the value, providing the data for the object, which is why it is called Constructor.
When discussing classes, one of the important topics is the constructor. Each class has at least one constructor. If we do not write a constructor explicitly for a class, then the Java compiler constructs a default constructor for that class.
Each time a new object is created, at least one constructor will be called. The main rule of constructors is that they have the same name as the class. A class can have more than one constructor.
The following is an example of how to built a constructor in java:
Rules to create Constructor in Java
There are two types of constructors: The first is the default constructor, which has no parameters. And the second type is the parameterized constructor.
In this example, we create a Constructor with no parameters in the Bike class. It will be summoned at the time the object is created.
Rule: If no constructor is defined in a class, the compiler automatically creates a default constructor.
Question: What is the purpose of the default constructor?
The default constructor provides default values for objects such as 0, null, and so on, depending on the type of data.
The default Constructor example that displays the default values
Explanation: In the above class, you do not create any Constructor, so the Compiler gives you a default Constructor. Here the values 0 and null are provided by the default constructor.
Question: Why use parametric constructor?
Parameterized constructors are used to provide different values for individual objects.
Example of parameterized constructor:
In this example, we create a Constructor of the Student class that has two parameters. We can have any number of parameters in the constructor.
Example of how to load the constructor in java
By Constructor
By assigning values of an object to another object.
By the clone () method of the Object class.
In this example, we copy the values of an object into another object by using Constructor in Java.
Question: Does Constructor return value?
Yes, that is the instance of the current class. (You can not use the return type, but it returns a value.)
Question: Can the constructor perform actions other than initialization?
Yes, like creating objects, starting a thread, calling a method, etc. You can perform any operation in the constructor as you would in a method.
To find out more about how to code if else statement in java:
When discussing classes, one of the important topics is the constructor. Each class has at least one constructor. If we do not write a constructor explicitly for a class, then the Java compiler constructs a default constructor for that class.
Each time a new object is created, at least one constructor will be called. The main rule of constructors is that they have the same name as the class. A class can have more than one constructor.
The following is an example of how to built a constructor in java:
Rules to create Constructor in Java
There are two types of constructors: The first is the default constructor, which has no parameters. And the second type is the parameterized constructor.
Default constructor in Java
This is a Constructor type without parameters. They have the following syntax:In this example, we create a Constructor with no parameters in the Bike class. It will be summoned at the time the object is created.
Rule: If no constructor is defined in a class, the compiler automatically creates a default constructor.
Question: What is the purpose of the default constructor?
The default constructor provides default values for objects such as 0, null, and so on, depending on the type of data.
The default Constructor example that displays the default values
Explanation: In the above class, you do not create any Constructor, so the Compiler gives you a default Constructor. Here the values 0 and null are provided by the default constructor.
Constructor is parameterized in Java
A constructor that has parameters called constructor is parameterized.Question: Why use parametric constructor?
Parameterized constructors are used to provide different values for individual objects.
Example of parameterized constructor:
In this example, we create a Constructor of the Student class that has two parameters. We can have any number of parameters in the constructor.
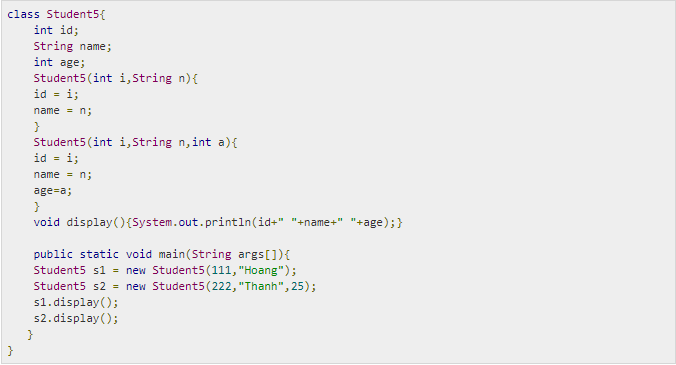
How to load the Constructor in Java with example
Overloading Constructor is a technique in Java in which a class can have any number of constructors that differ in parameter lists. The compiler distinguishes between these constructors by analyzing the number of parameters in the list and their types.Example of how to load the constructor in java
How to copy Constructor in Java with example
In Java there is no Copy Constructor like in C ++. However, you can copy the values of an object to another object. There are many ways to perform the copying of values, which are:By Constructor
By assigning values of an object to another object.
By the clone () method of the Object class.
In this example, we copy the values of an object into another object by using Constructor in Java.
Copy the values without using Constructor
We can copy the values of an object into another object by assigning the values of that object to another object. In this case, we do not need to create the Constructor.Question: Does Constructor return value?
Yes, that is the instance of the current class. (You can not use the return type, but it returns a value.)
Question: Can the constructor perform actions other than initialization?
Yes, like creating objects, starting a thread, calling a method, etc. You can perform any operation in the constructor as you would in a method.
To find out more about how to code if else statement in java:








Comments
Post a Comment